ISO 22000 Certification: Establishing a Robust Food Safety Management System
ISO 22000 is an internationally recognized standard that enables organizations to establish an effective Food Safety Management System (FSMS). It ensures that food safety is maintained throughout the supply chain, from farm to fork, by systematically identifying and controlling food safety hazards.
The standard integrates the principles of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) with other essential elements of food safety management. By implementing ISO 22000, organizations can ensure that all potential hazards in food production and handling are identified, assessed, and effectively controlled.
ISO 22000 not only focuses on food safety but also emphasizes the quality and consistency of processes. The structured approach outlined in the standard supports organizations in prioritizing food safety at every level of operation and demonstrates their commitment to maintaining control over food safety risks.
The primary objective of ISO 22000 is to eliminate the presence of hazardous substances in food products and to ensure that food reaching the consumer is safe. This enhances consumer trust, improves regulatory compliance, and opens up new market opportunities by meeting international food safety expectations.
What are the steps to get ISO 22000 Certification?
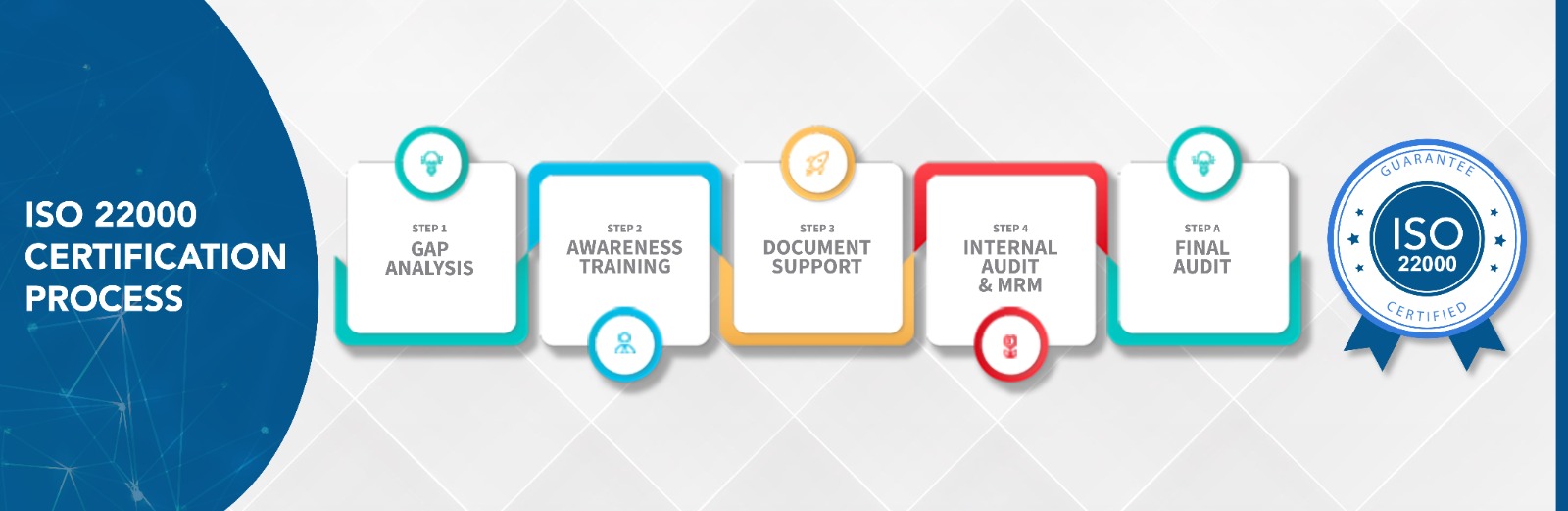
Any organization involved in the food chain must recognize the critical importance of food safety. During the implementation of a Food Safety Management System (FSMS), the principles of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) are applied alongside Prerequisite Programs (PRPs) to ensure comprehensive control over food safety risks
Objectives of ISO 22000 certification:
Benefits and Objectives of Achieving ISO 22000 Certification
Achieving ISO 22000, the internationally recognized standard for Food Safety Management Systems (FSMS), enables organizations to meet essential objectives related to food safety and quality. Below are the key benefits and goals of implementing ISO 22000:
1. Deliver Safe Products and Enhance Customer Satisfaction
Ensures that the products and services provided by the organization are safe for consumption and do not pose any risk to public health.
Builds customer trust and enhances satisfaction by consistently delivering safe and high-quality products.
2. Comply with Food Safety Policies
Supports adherence to the organization’s food safety policy.
Demonstrates the organization’s commitment to food safety to all interested parties, including customers, regulators, and stakeholders.
3. Develop and Maintain a Food Safety Management System
Plan and implement an effective FSMS tailored to the organization’s processes.
Operate and maintain the FSMS to ensure continuous performance and control.
Improve and update the FSMS regularly to adapt to changes and enhance food safety practices.
4. Ensure Compliance with External Safety Requirements
Establish and demonstrate conformity with food safety requirements set by external authorities.
Ensure compliance with applicable legal and regulatory food safety standards.
Fulfill statutory obligations related to food safety.
5. Promote Effective Communication Throughout the Food Supply Chain
Communicate food safety requirements and issues with customers, suppliers, and other interested parties involved in the food chain.
Foster transparency and collaboration across all stakeholders to strengthen food safety culture and performance.
What is ISO 45001 certification in general?
High-Level Structure of ISO Standards and Key Clauses in ISO 45001
International standards published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) follow a unified format known as the High-Level Structure (HLS). Introduced in 2013, this structure provides a consistent framework comprising 10 standardized clauses, making it easier for organizations to implement and integrate various ISO management systems.
ISO 45001, which focuses on Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems (OHSMS), adopts this high-level structure. The standardized framework simplifies implementation for both employees and consultants by offering a clear and consistent approach. The key clauses of ISO 45001 include:
1. Context of the Organization
This clause involves identifying internal and external factors that can affect the OHSMS. Understanding the organization’s context helps in defining the scope and ensuring that all relevant issues are considered when designing the system.
2. Leadership
Leadership plays a critical role in the success of OHSMS. This clause ensures that top management demonstrates commitment by establishing clear policies, setting objectives, and defining roles and responsibilities. It emphasizes accountability and the promotion of a culture of safety throughout the organization.
3. Planning
Planning involves identifying risks and opportunities related to occupational health and safety. It includes setting objectives and determining actions to mitigate risks and enhance opportunities. The top management is actively involved in shaping these plans to ensure effective implementation.
4. Support, Operation, Performance Evaluation, and Improvement
Other clauses—such as support, operation, performance evaluation, and continual improvement—are equally important and build upon the foundation laid in the initial phases. They ensure that resources are available, processes are properly managed, performance is regularly reviewed, and improvements are consistently made.
It is important to note that explaining every aspect of ISO 45001 in a single overview is not possible due to the standard’s depth and complexity. For a more detailed understanding and expert guidance tailored to your organization’s needs, you can contact TCERTGLOBAL, a trusted provider of ISO consulting services.
What are the benefits of implementation of ISO 22000 standard in an organisation?
Benefits of Implementing a Food Safety Management System (FSMS) Based on ISO 22000
Implementing a Food Safety Management System (FSMS) aligned with the ISO 22000 standard brings a wide range of organizational benefits, particularly in enhancing food safety, operational efficiency, and stakeholder trust. Below are the key advantages:
1. Improved Communication and Coordination
Strengthens communication both between departments and within departments, ensuring everyone is aligned on food safety protocols and responsibilities.
Enhances coordination among teams, contributing to smoother operations and better collaboration.
2. Elimination of Foodborne Hazards
Helps identify and eliminate any disease-causing elements in food, significantly reducing the risk of contamination and foodborne illnesses.
Establishes robust hazard control measures throughout the food production and handling processes.
3. Increased Operational Efficiency
Boosts the performance and productivity of employees by providing clear processes and responsibilities.
Promotes a systematic and structured approach through well-defined Prerequisite Programs (PRPs) to maintain food safety and quality.
4. Global Recognition and Compliance
ISO 22000 is a globally recognized standard that fulfills comprehensive food safety requirements for organizations of any size or type.
Supports compliance with government regulations and international food safety laws, reducing the risk of legal issues.
5. Cost Savings and Resource Optimization
Prevents duplication of efforts, optimizes resource usage, and preserves operational costs.
Enhances financial stability by building customer trust and loyalty, especially after consistent delivery of safe and quality food products.
6. Enhanced Reputation and Market Credibility
Strengthens the organization’s reputation and brand value by demonstrating a commitment to food safety.
Improves reliability and consumer confidence in the safety and quality of products.
7. Continual Improvement Culture
Encourages a culture of continuous improvement by helping the organization identify opportunities for growth and efficiency.
Reduces operational costs through proactive quality control and process improvement.
8. Stronger Supplier and Stakeholder Relationships
Facilitates better relationships with suppliers, partners, and other interested parties by clearly defining food safety expectations.
Enhances employee engagement and internal communication, ensuring everyone understands their role in maintaining food safety.
